Multi-Layer Perceptron
This guide will help you build a 3 layer Neural Network from scratch i.e without the use of any existing python libraries.
A Neural Network generally takes the form:
-
Input Layer
-
Hidden Layer(s)
-
Output Layer
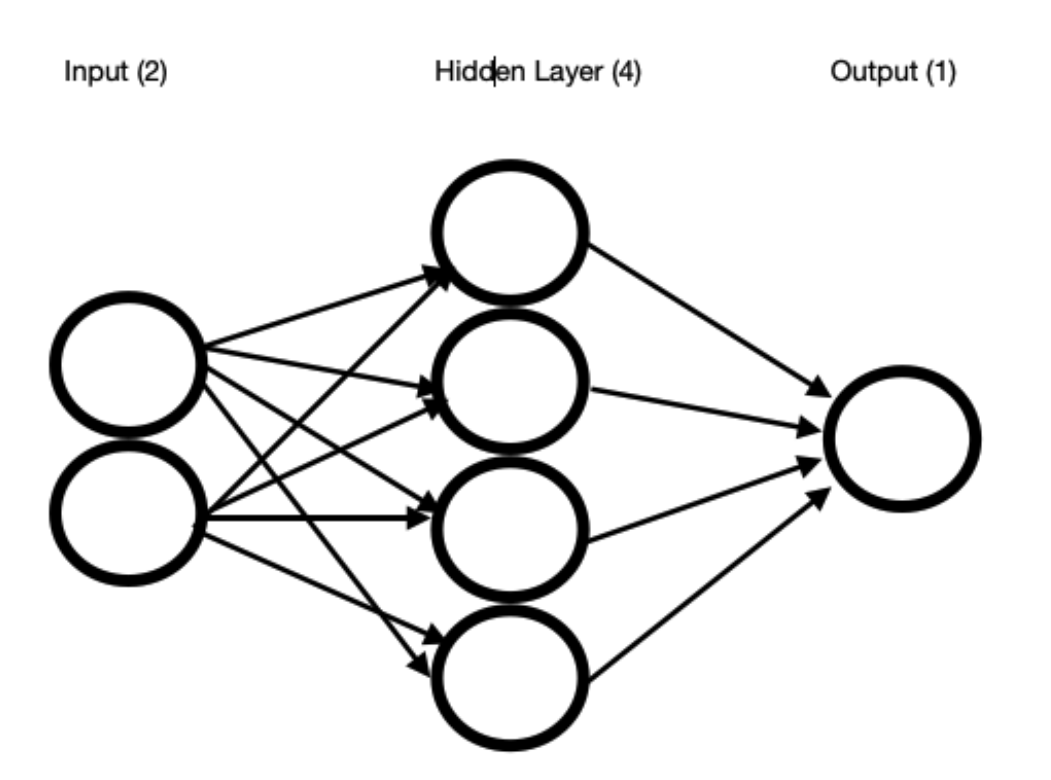
For this tutorial we will implement a 3 layer NN with 2-\(n_h\)-1 architecture where \(n_h\) stands for the number of hidden nodes.
Some specifications:
-
Activation function used: Sigmoid
-
Learning Rate: 0.005
-
Number of hidden nodes, \(n_h\) = 2,4,6,8,10
-
Error: Mean Squared Error
Step 1: Load the given train and test datasets.
Step 2: Feature normalize your train and test datasets:
For each feature \(x_i\) , your normalized feature \(y_i\) will be:
yi = (xi - mi)/si
where \(m_i\) is the mean and \(s_i\) is the standard deviation of the given feature.
Use the same \(m_i\) and \(s_i\) values to normalize your test dataset. Remember, you only transform your test dataset with these values and not fit it using its own mi and si values.
Step 3: Split the train dataset into train and validation sets (an 80/20 split should work)
Step 4: The Multi Layer Perceptron Class and functions:
Our sigmoid activation function and it’s derivatives are defined as follows:
def sigmoid(t):
return 1/(1+np.exp(-t))
def sigmoid_derivative(g):
return g * (1 - g)
Our Multi-Layer Perceptron Class is defined as follows:
class MultiLayerPerceptron:
def __init__(self, x, y,nh):
self.input = x
#random weight initialization
self.weights1 = np.random.rand(self.input.shape[1],nh)
#random weight initialization
self.weights2 = np.random.rand(nh,1)
self.y = y
self.output = np.zeros(self.y.shape)
def feedforward(self):
self.layer1 = sigmoid(np.dot(self.input, self.weights1))
self.output = sigmoid(np.dot(self.layer1, self.weights2))
return self.output
def backpropagation(self):
'''
This function calculates new weight vectors and updates
the weight for both input
to hidden as well as hidden to output layers.
'''
del_w2 = np.dot(self.layer1.T, (2*(self.y - self.output)
* sigmoid_derivative(self.output)))
del_w1 = np.dot(self.input.T, (np.dot(2*(self.y -
self.output) * sigmoid_derivative(self.output),
self.weights2.T) * sigmoid_derivative(self.layer1)))
# weight update rule (negative sign changes to positive.
# because of a negative sign in derivative calculation)
self.weights1 += 0.0005*del_w1
self.weights2 += 0.0005*del_w2
def train(self, X, y):
self.output = self.feedforward()
self.backpropagation()
def validation(self,x):
'''
This function is used to test the validation test samples
using the above updated weights.
'''
self.l1 = sigmoid(np.dot(x, self.weights1))
self.out = sigmoid(np.dot(self.l1, self.weights2))
return self.out
Step 5: Stopping Criterion:
The model stops training when the validation loss no longer changes. The below code snippet implements the same.
while True:
iteration += 1
print ('--------------Iteration #{}--------------
'.format(iteration))
# training loss
training_loss.append(np.mean(np.square(trainY -
MLP.feedforward())))
print ("Loss: ",np.mean(np.square(trainY -
MLP.feedforward()))) # mean squared error
# val loss before training the model
prev_val_loss = np.mean(np.square(valY -
MLP.validation(valX)))
MLP.train(trainX,trainY)
# val loss after training the model
new_val_loss = np.mean(np.square(valY -
MLP.validation(valX)))
print ('Validation loss: ',new_val_loss)
validation_loss.append(new_val_loss)
# test loss using the updated weights
test_loss_.append(np.mean(np.square(testY -
MLP.validation(testX))))
# if the validation loss doesn't decrease/change
further, then stop.
if (prev_val_loss-new_val_loss)<0.000001:
break
Step 6: Final test loss using the new weights:
test_loss = np.mean(np.square(testY-MLP.get_test_output(testX)))
Step 7: Train and Test Accuracies:
# test accuracy
correct = 0
for row,label in zip(testX,testY):
if MLP.get_test_output(row)>0.5 and label==1.0:
correct+=1
elif MLP.get_test_output(row)<0.5 and label==0.0:
correct+=1
print ('Test Accuracy: {}'.format(correct/len(testX)))
#Training Accuracy Calculation
correct = 0
for row,label in zip(trainX,trainY):
if MLP.get_test_output(row)>0.5 and label==1.0:
correct+=1
elif MLP.get_test_output(row)<0.5 and label==0.0:
correct+=1
print ('Training Accuracy {}'.format(correct/len(trainX)))
Step 8: Train and Test Plots
plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(training_loss,label='train')
plt.plot(validation_loss,label='validation')
plt.plot(test_loss_,label='test')
plt.show()
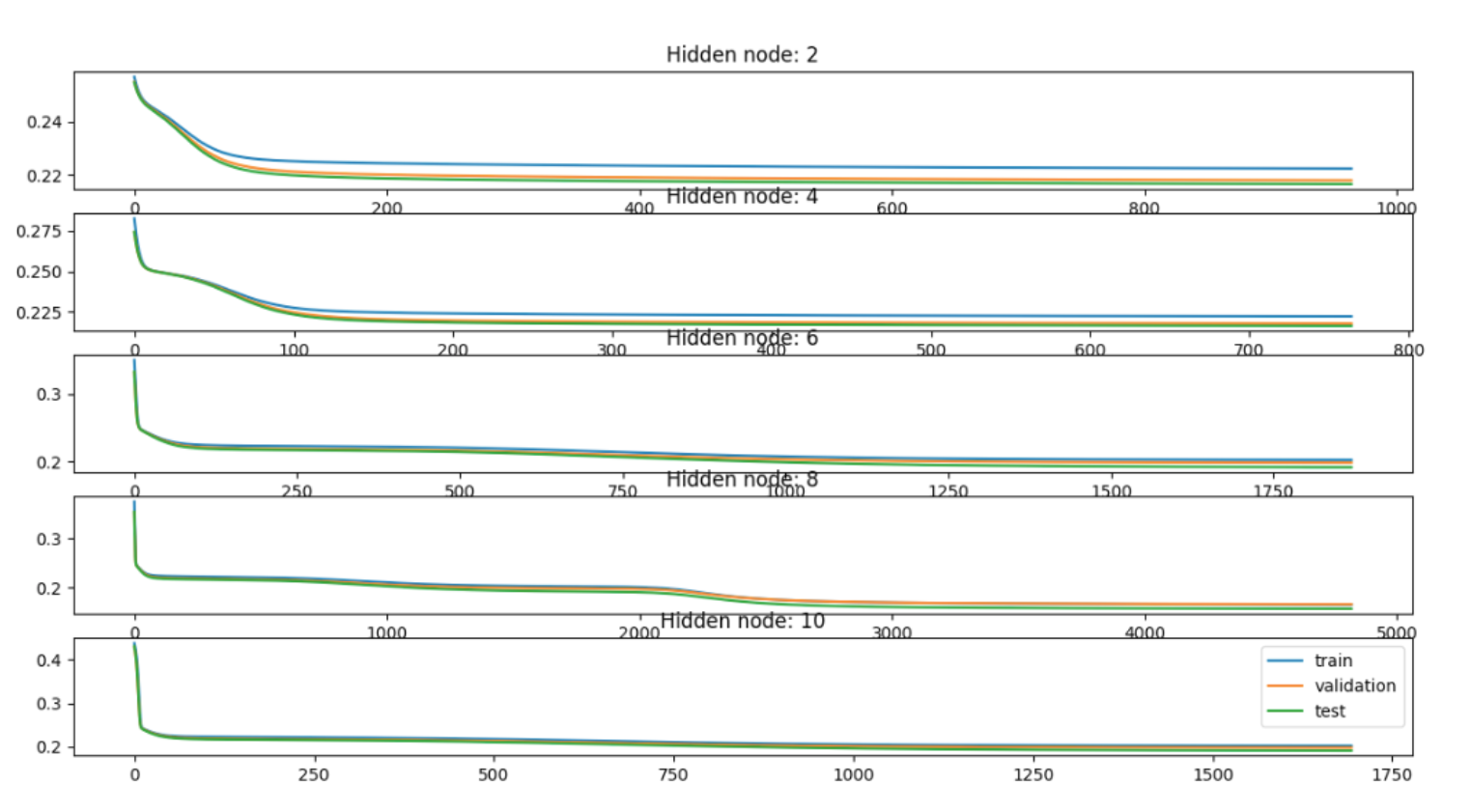
The below learning curves correspond to different number of hidden nodes (2,4,6,8 and 10).